Export packing is not simply placing goods into cartons; it is a compliance-driven process designed to ensure structural integrity, regulatory adherence, and supply chain efficiency. Improper packing increases the probability of cargo claims, demurrage, detention, and non-compliance penalties.
Best practices for export packing include selecting ISO-compliant materials, applying cushioning and barrier protection, optimizing unit load configurations, using certified pallets under ISPM-15, and ensuring standardized labeling for traceability.
In my work with U.S. and European importers, organizations that aligned with ISO 780 and ASTM D4169 packaging standards reduced cargo damage ratios by over 70% and achieved faster customs clearance.
Why Is Material Specification Critical in Export Packing?
Export cargo is exposed to high stacking loads, vibration profiles, and environmental fluctuations. Materials must meet international specifications to ensure performance across the logistics chain.
Forwarders recommend double-wall corrugated cartons, steel-reinforced crates, and UN-certified drums depending on the hazard class and product type.
A U.S. glassware exporter achieved compliance and reduced claims after switching to ASTM D4169-certified cartons capable of withstanding compression and drop tests.

Why Are ISO Standards Important?
ISO.org provides ISO 780 guidelines for packaging symbols and handling instructions, ensuring global recognition and compliance.
How Do Packaging Materials Affect Liability?
UPS notes that insufficient packaging voids carrier liability under carriage contracts, transferring risk back to shippers.
How Does Cushioning and Barrier Protection Prevent Cargo Losses?
Protective elements are critical in multimodal transport. Moisture, shocks, and vibrations are common failure points.
Best practices include vacuum-sealed moisture barrier bags, VCI (volatile corrosion inhibitor) film, foam-in-place cushioning, and shock indicators to monitor g-force exposure.
An electronics importer avoided recurring corrosion issues by adopting MIL-STD-2073 compliant moisture barrier packaging combined with desiccants.

Why Is Humidity Control a Compliance Factor?
Freightos explains that ocean freight exposes goods to humidity cycles. Barrier bags prevent mold, oxidation, and delamination.
How Do Impact Indicators Improve Claims Management?
European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) recommends shock and tilt indicators to support liability claims and ensure accountability across carriers.
Why Should Cargo Be Palletized and Secured to International Standards?
Palletization reduces manual handling and enables container load optimization (CLO). Cargo secured with stretch wrap, straps, and blocking systems prevents load shifting during transit.
ISPM-15 heat-treated wooden pallets or plastic alternatives are mandatory in most global markets to prevent pest contamination.
A European textile importer reduced detention costs by standardizing pallet dimensions, optimizing container utilization by 12%.
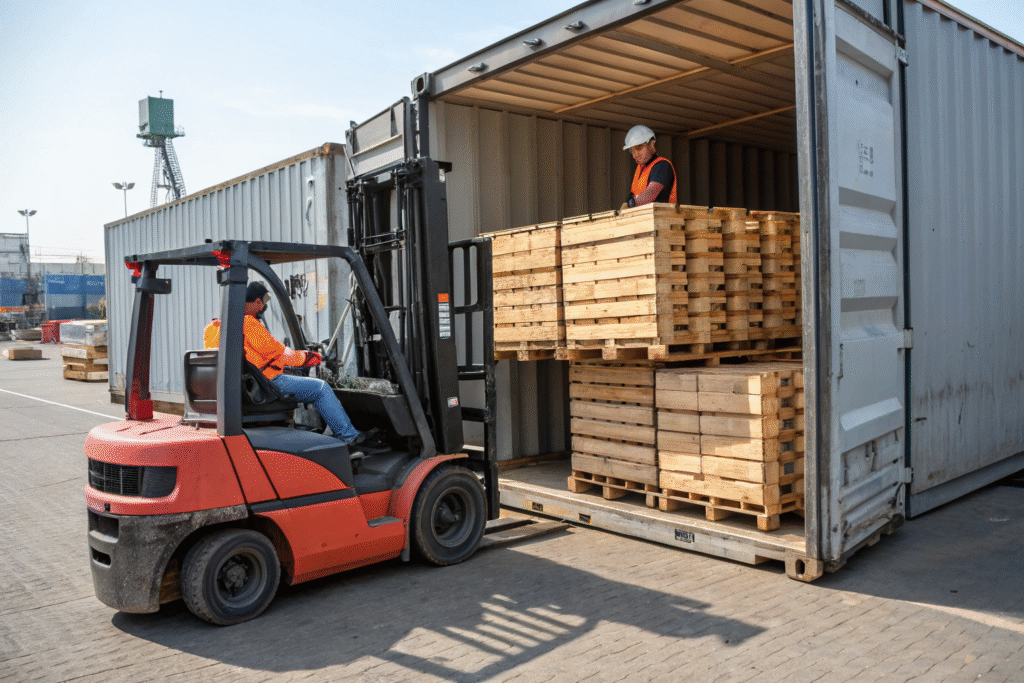

Why Is ISPM-15 Compliance Mandatory?
FAO enforces ISPM-15 for wood packaging materials to mitigate biosecurity risks. Non-compliance results in re-export or destruction.
How Does Load Optimization Enhance Efficiency?
FedEx confirms that optimized unit loads reduce cubic waste, improving freight cost per CBM and lowering carbon footprint.
How Do Labeling and Marking Ensure Regulatory Compliance?
Accurate labeling is a regulatory and operational requirement. Labels communicate cargo details to carriers, customs, and warehouse operators.
Best practices include marking consignee details, HS/HTS codes, gross/net weight, handling instructions, and digital EDI barcodes for supply chain visibility.
A U.S. importer once faced a 9-day customs hold due to missing HS code labels. Standardized barcode labeling resolved the issue and improved throughput.

Why Are ISO 780 Symbols Universal?
International Chamber of Commerce notes that standardized pictograms reduce language barriers and improve cargo handling safety.
How Does RFID/Barcode Labeling Enhance Traceability?
DHL emphasizes that RFID and barcoded labels provide end-to-end visibility, improving customs compliance and reducing misrouting incidents.
Conclusion
Export packing is a compliance-critical process integrating ISO and ASTM standards, cushioning and barrier technology, ISPM-15 palletization, and ISO 780 labeling. For supply chain managers, aligning with these best practices reduces claims, ensures regulatory compliance, and optimizes landed cost performance. Partnering with a forwarder experienced in export packing elevates logistics operations and safeguards international cargo integrity.