When one of our clients had a vessel rerouted around Africa due to piracy threats, adding 14 days and $85,000 in additional costs, the reality of modern maritime piracy became undeniable. As founder of GeeseCargo with extensive risk assessment experience, I've learned that piracy isn't the swashbuckling adventure of movies—it's a sophisticated criminal enterprise that directly impacts shipping costs, schedules, and crew safety.
The piracy threat varies dramatically by route, with high-risk areas including the Gulf of Guinea, Singapore Strait, and certain South American waters. While Somali piracy has significantly decreased, West African piracy now accounts for over 95% of crew kidnappings globally. The financial impact extends beyond ransoms to include insurance premiums, security costs, and route diversions that can increase shipping costs by 15-40% in affected regions.
Piracy risk assessment requires understanding both current threat patterns and the underlying economic, political, and social drivers that create piracy hotspots. Companies that systematically address piracy threats typically experience fewer disruptions and lower insurance costs while maintaining crew safety.
What Are the Current Global Piracy Hotspots?
Piracy threats have shifted significantly over the past decade, with new regions emerging as concerns while traditional hotspots have improved.
How Dangerous Is the Gulf of Guinea Currently?
The Gulf of Guinea remains the world's most dangerous piracy region, accounting for 43% of all reported piracy incidents in 2023. This area sees sophisticated operations targeting vessels for cargo theft and, more commonly, crew kidnapping for ransom.
Attack methodology has evolved to include mothership operations. Pirates operate far from shore using hijacked fishing vessels as floating bases, enabling attacks up to 200 nautical miles offshore.
Kidnapping-for-ransom is the primary business model. Rather than stealing cargo, most Gulf of Guinea pirates focus on taking crew members hostage, with average captivity periods of 20-40 days while ransoms are negotiated.
What Are the Emerging Threats in Southeast Asia?
The Singapore Strait has seen a significant increase in petty piracy and armed robbery. While less violent than West African piracy, these incidents involve boarding anchored or slow-moving vessels to steal equipment and cargo.
Product tankers and bulk carriers are primary targets. Pirates in Southeast Asia typically target specific cargoes like marine gas oil or valuable equipment rather than pursuing kidnapping schemes.
Low-level but high-frequency incidents create operational challenges. While most Southeast Asian piracy doesn't involve violence against crew, the frequency of incidents requires constant vigilance and security measures.
How Does Piracy Impact Shipping Operations and Costs?
The consequences of piracy extend far beyond the immediate danger to vessels and crew to affect overall supply chain economics.

What Are the Direct Financial Impacts of Piracy Risk?
War risk insurance premiums increase 10-50x in high-risk areas. Vessels transiting designated high-risk areas pay substantial additional premiums, with some routes seeing insurance costs increase from $500 to $25,000 per voyage.
Security equipment and personnel add significant costs. Armed security teams, citadels (safe rooms), and physical deterrent systems can cost $15,000-$50,000 per transit depending on risk level.
Route diversions dramatically increase fuel and time costs. Avoiding high-risk areas by taking longer routes, such as sailing around South Africa instead of through the Gulf of Guinea, can add 7-14 days and $80,000-$150,000 per voyage.
How Do Piracy Threats Affect Scheduling and Reliability?
Vessel speed increases in dangerous areas burn additional fuel. Ships often transit at maximum speed through high-risk zones, increasing fuel consumption by 20-40% during these segments.
Port call sequencing may change to avoid nighttime arrivals. Arriving during daylight hours in certain ports reduces vulnerability but requires careful schedule management and potential delays.
Crew concerns impact operations and retention. Experienced officers increasingly refuse voyages through high-risk areas, creating staffing challenges and requiring hazard pay premiums.
What Practical Measures Can Mitigate Piracy Risks?
Proactive security measures significantly reduce piracy vulnerability when properly implemented and maintained.
What Physical Security Measures Provide the Best Protection?
Citadels (secure rooms) have proven highly effective against boarding. These reinforced spaces with independent communications allow crew to shelter safely until naval assistance arrives.
Physical barriers prevent boarding attempts. Razor wire, electric fences, water cannons, and anti-boarding obstacles make successful piracy attacks significantly more difficult.
Enhanced lighting and surveillance improve detection. Powerful lights, night vision equipment, and thermal cameras make vessels less attractive targets by increasing detection likelihood.
How Effective Are Best Management Practices (BMP5)?
BMP5 compliance reduces attack success rates by over 80%. Following the latest Best Management Practices guidelines, including specific transit preparations and threat responses, dramatically improves vessel security.
Watchkeeping and vigilance are the first line of defense. Maintaining proper lookouts, conducting piracy drills, and implementing 24/7 bridge watches significantly improve early threat detection.
Communication protocols ensure rapid assistance. Regular position reporting to naval forces and security centers enables quicker response during actual incidents.
How Should You Assess Piracy Risk for Specific Routes?
Systematic risk assessment enables informed decisions about routing, security measures, and insurance requirements.

What Factors Determine Route-Specific Piracy Risk?
Historical incident data provides the foundation for risk assessment. Analyzing piracy incidents over the previous 24-36 months reveals patterns, methodologies, and success rates for specific routes.
Local political and economic conditions drive piracy activity. Regions with poor governance, high unemployment, and limited alternative livelihoods typically experience higher piracy rates.
Naval presence and law enforcement capability affect deterrence. Areas with active naval patrols, information sharing networks, and prosecutorial capability demonstrate lower piracy success rates.
How Can You Access Current Piracy Threat Information?
Maritime security organizations provide real-time advisories. Services like the Maritime Security Centre - Horn of Africa, UKMTO, and various private intelligence providers offer current threat assessments.
Industry associations share collective security information. Organizations like BIMCO, ICS, and INTERTANKO circulate timely warnings and best practices based on member reporting.
Flag state and coastal nation advisories offer official guidance. National maritime administrations typically issue specific guidance for vessels flying their flags or transiting their waters.
What Insurance and Contractual Considerations Apply?
Piracy risks necessitate specific insurance coverage and contractual protections to manage financial exposure.

What Insurance Coverage Addresses Piracy Risks?
War Risk P&I insurance covers third-party liabilities. This additional coverage protects against claims for injury, environmental damage, or other liabilities arising from piracy incidents.
Kidnap and Ransom insurance provides specialized response resources. Beyond financial coverage, K&R policies typically include crisis response consultants, negotiators, and medical support.
Hull war risk policies cover physical damage. Separate from standard hull insurance, these policies cover damage from piracy attacks, including explosives and weapon impacts.
How Should Contracts Address Piracy Risks?
BIMCO piracy clauses allocate costs and responsibilities. Standard contract clauses clearly define which party bears additional costs for security, route diversions, and delays due to piracy threats.
Force majeure provisions may apply to piracy-related disruptions. Depending on jurisdiction and specific contract language, piracy incidents might trigger force majeure clauses relieving performance obligations.
Security cost allocation should be explicitly defined. Contracts should specify whether owners or charterers bear costs for guards, equipment, and additional insurance premiums.
What Are the Legal and Regulatory Considerations?
Piracy response involves complex international legal frameworks that affect everything from armed security to incident prosecution.
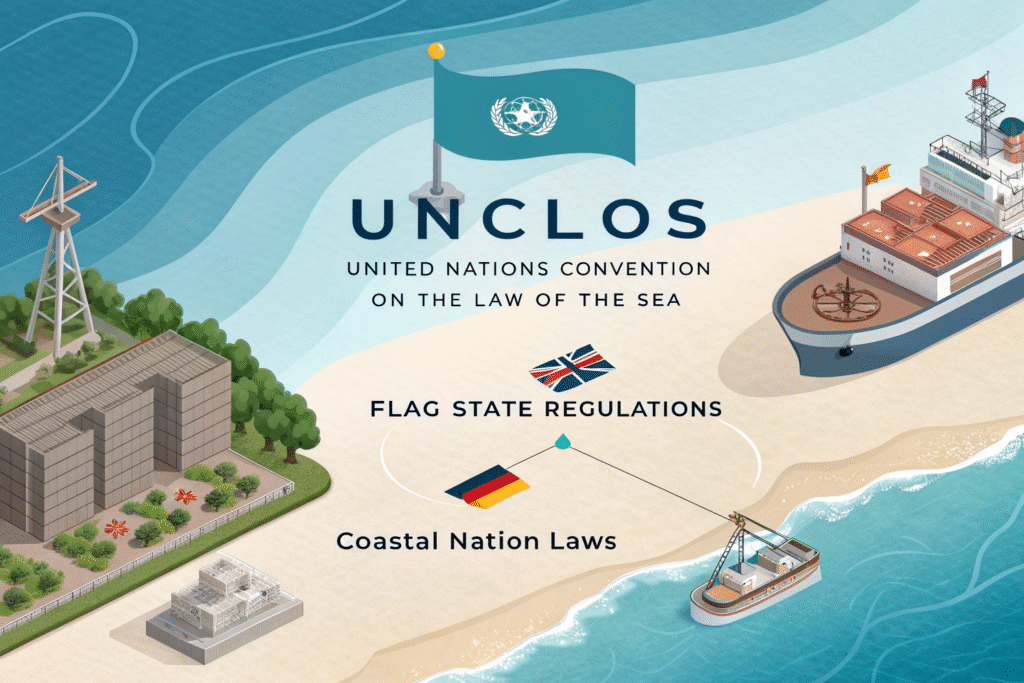
How Do International Laws Govern Piracy Response?
UNCLOS defines piracy and enforcement rights. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea establishes universal jurisdiction for piracy incidents occurring on the high seas.
SUA Convention addresses maritime terrorism overlaps. The Suppression of Unlawful Acts against the Safety of Maritime Navigation protocol covers incidents that might not meet strict piracy definitions but pose similar threats.
Regional agreements enable coordinated response. Agreements like the Djibouti Code of Conduct facilitate information sharing and capacity building in high-risk regions.
What Regulations Govern Private Maritime Security?
Flag state authorization typically required for armed guards. Most countries require specific permission for vessels flying their flag to employ armed security teams.
Weapons transportation laws vary significantly between ports. Countries have different regulations regarding weapons embarkation/disembarkation, storage, and transportation.
Use of force protocols must be clearly established. Security teams should operate under Rules for the Use of Force that are compliant with both flag state laws and international standards.
Conclusion
Piracy remains a serious and evolving threat that requires continuous assessment and adaptive security measures. While the nature of piracy has changed from the Somali model that dominated a decade ago, new hotspots and methodologies have emerged that demand vigilant attention. The most successful shipping companies treat piracy not as an isolated security issue but as an integrated operational consideration affecting routing, scheduling, costing, and risk management.
At GeeseCargo, we've helped clients reduce piracy-related disruptions by over 70% through systematic risk assessment and proactive security planning. The key is recognizing that piracy risk management requires balancing security, cost, and operational efficiency rather than seeking to eliminate risk entirely.
Begin your piracy risk management by conducting a thorough assessment of your specific routes and vessel types, then implement appropriate security measures based on credible threat assessments. Remember that in piracy risk management, preparation and prevention are dramatically more effective than reaction—the modest investment in security measures and planning typically returns many times over in avoided disruptions, costs, and potential tragedies.









