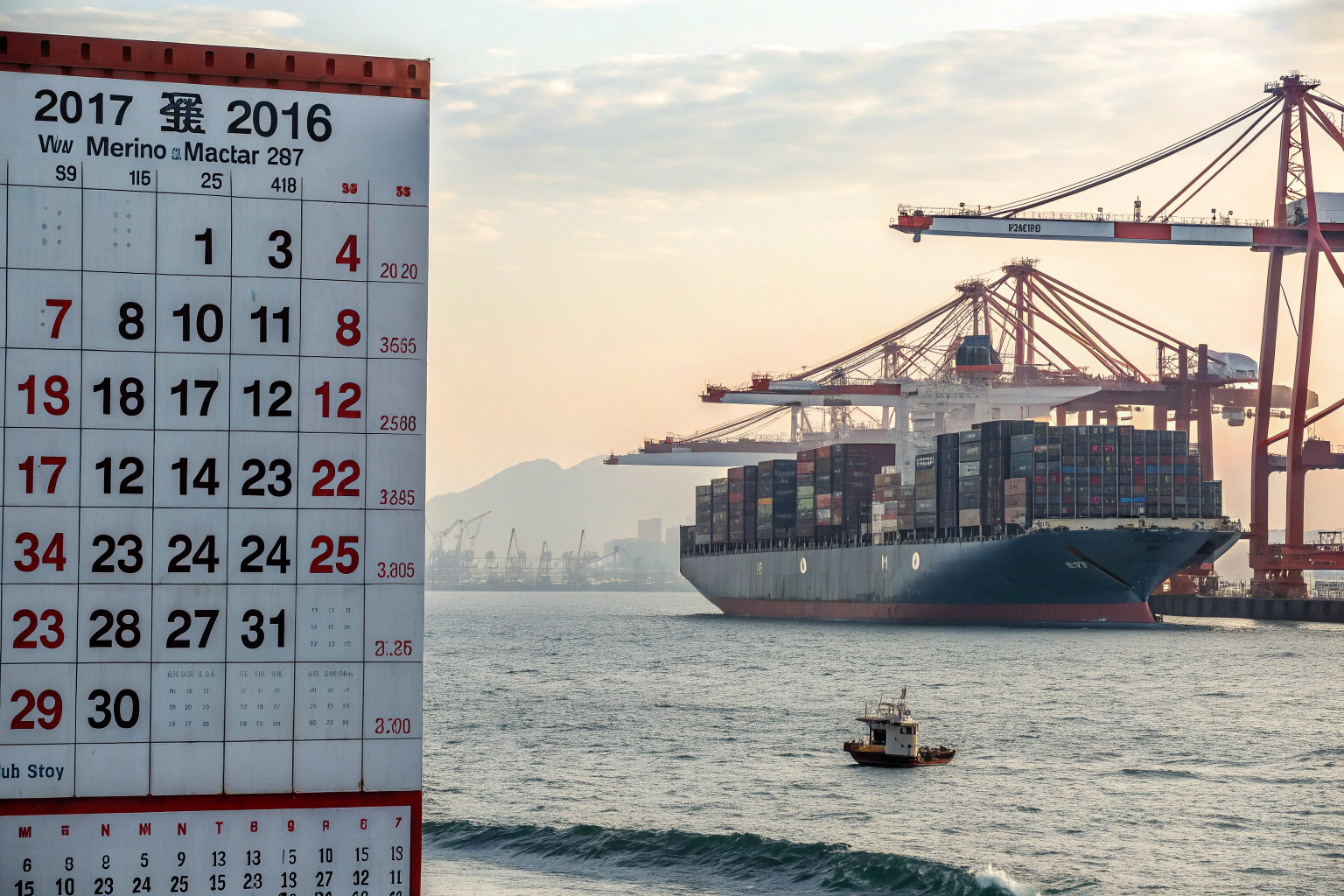
Whenever I meet new clients, the question almost always comes up: “How long does it actually take by sea from China to the U.S.?” Honestly, I wish I could give one neat answer. Well, sometimes it’s fast, sometimes it feels painfully slow. In my experience, the unpredictability surprises people more than the costs.
On average, sea freight takes about 15 to 40 days, depending on whether you’re shipping to the West Coast or the East Coast, and depending on customs, weather, and a few other factors that nobody really controls.
From my observation, the sailing itself is only one piece of the puzzle. The waiting, the handling, the customs clearance—that’s where days get added quietly. I’ve had shipments that technically crossed the ocean in record time, but then sat at the port for a week just waiting for paperwork.
What Is the Average Transit Time for Sea Freight?
People always want the “average” time, but the truth is, it depends heavily on where your goods are going.
Typically, shipments from China to the U.S. West Coast take about 15–20 days. If you’re sending to the East Coast, it’s usually 25–40 days.
I remember once, a shipment of electronics from Shenzhen to Los Angeles landed in just 16 days. Another time, a client’s clothing shipment to New York stretched out to 36 days. Same origin, same season—completely different outcomes. That’s why I never promise a single number.

How Fast Is Shipping to the West Coast?
Well, West Coast is the faster option. Carriers like COSCO Shipping or Maersk can usually make the trip in two to three weeks. For importers who want a balance between speed and cost, this is often the sweet spot.
Why Does the East Coast Take Longer?
Because the route is longer—ships go through the Panama Canal or sometimes the Suez. According to Hapag-Lloyd schedules, those trips stretch to 28–40 days. And honestly, East Coast ports like New York often face more congestion too, which doesn’t help.
What Steps Add Time Beyond Sailing?
When shippers think of “transit time,” they usually picture only the days on water. Actually, that’s just part of the story.
Port handling, trucking, consolidation, and customs can add another 5–10 days.
I think this is where most first-time importers get caught off guard. One client told me, “The ship arrived in 19 days, but why did it take 28 to get to my warehouse?” The answer: customs inspections and terminal delays. It’s frustrating, but very common.

How Does Customs Clearance Impact Time?
If your paperwork is complete, customs may clear your cargo in a day or two. But if there’s a mistake? CBP explains that formal entries can stretch longer, sometimes 5–7 days. I’ve seen a shipment held just because the invoice had the wrong product description. Small errors, big delays.
What About Port Congestion?
Congestion is a headache. At busy ports like Los Angeles, ships sometimes sit outside for days. Port of Los Angeles updates often mention delays of 2–5 days when too many vessels arrive at once. From my observation, even the most punctual vessel can’t fight a traffic jam on the water.
How Do Routes and Seasons Affect Shipping Time?
It’s not just distance. Seasons, routes, and weather matter a lot. And surprisingly, they matter more than most people realize.
Peak seasons like Chinese New Year or the U.S. holiday rush, plus storms or canal delays, can add 5–15 extra days.
From my observation, shipments before Chinese New Year almost always take longer. Everybody’s rushing cargo out at the same time. I usually tell clients, “Book early or be ready to wait.”
How Do Peak Seasons Impact Transit?
Well, demand spikes lead to overbooked vessels. According to Freightos, shipping in peak season can delay containers by more than a week. I’ve seen it myself—clients who booked too late had to wait for the next sailing.
Do Weather and Canal Routes Really Matter?
Yes, without a doubt. Storms in the Pacific can force ships to slow down. And when there’s trouble at the Panama Canal, like drought restrictions recently reported by Reuters, ships either wait longer or reroute. Either way, days get added.
How Can You Plan Better for Sea Freight Timelines?
While you can’t control everything, you can plan around the risks.
The smartest importers book early, add buffer days, use shipment tracking, and work with forwarders who can anticipate delays.
In my experience, the worst mistake is planning around the “best-case scenario.” I always tell clients: leave one to two weeks of buffer. That extra cushion can mean the difference between meeting a deadline or missing it completely.

Should You Always Rely on Forwarders?
I think yes, especially if you’re not shipping huge volumes. Forwarders track not just your container but also the conditions at ports. With platforms like project44 and Flexport, the data is better than ever. But someone still has to explain it, and that’s what forwarders do.
Is Air Freight a Better Alternative?
Sometimes, yes. If your delivery can’t wait, air freight is the safer option, even if it costs more. According to IATA Cargo, air shipments usually take 3–7 days. Some of my clients split shipments—send part by air to keep business moving and the rest by sea to save money.
Conclusion
So, how long does sea freight from China to the USA take? Honestly, anywhere between 15 and 40 days. Sometimes faster, sometimes slower—it depends on too many moving pieces.
As someone who’s managed shipments for years, I’ve seen both extremes: one container made it in 15 days flat, another dragged on for 45 thanks to congestion and customs. That’s why planning buffer time and trusting the right logistics partner isn’t just good practice—it’s survival.









